Benefits
High volumes of traffic can quickly cause a single-lane roundabout to saturate. While a multi-lane roundabout solves capacity challenges in areas where the volume of traffic is important, it also compromises safety! The turbo-roundabout addresses both the capacity and safety challenges thanks to the characteristics listed below.
|
Limited Weaving Movements
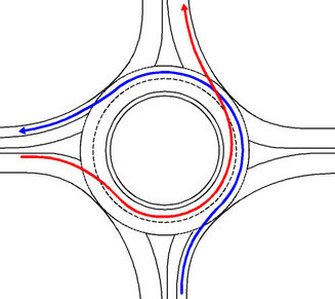
A turbo-roundabout doesn't allow drivers to change lanes on the circulatory area, but forces them to choose the entry lane according to their exit direction. Limited weaving maneuvers results in a safety increase on the roundabout. Research and experiments show that traffic accidents are reduced by 72% on turbo-roundabouts compared to multi-lane roundabouts. Increased Capacity
Maintaining a low driving speed on the roundabout doesn't necessarily lower its capacity. By ensuring a low driving speed as well as a safe and sustainable traffic flow, the capacity of a turbo-roundabout remains as efficient as of a multi-lane roundabout. |
|
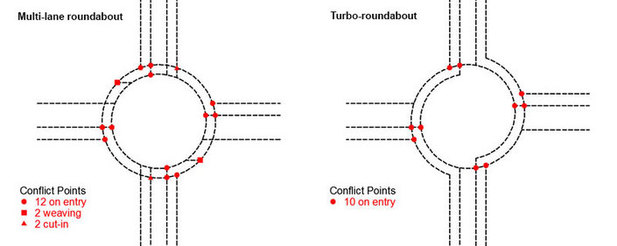
Fewer Conflict Points
By introducing nested spiral lanes, disabling lane changes on the circulatory area and by forcing vehicles to exit, – thanks to lane markings or raised lane dividers – the number of conflict points on a turbo-roundabout is clearly reduced. Therefore, traffic accidents as less likely to take place on a turbo than on a multi-lane roundabout. |
Lower Vehicle Speed
With various tools – raised or non-raised lane dividers, simple lane markings, – a turbo-roundabout is channeling vehicle movements in a narrower area than a regular multi-lane roundabout. In other words, vehicles' driving speed on the circulatory lane is lowered to guarantee maximum safety. Various research and experiments show that traffic accidents are reduced by 72% on turbo-roundabouts compared to multi-lane roundabouts, which makes turbo-roundabouts nearly as safe as single lane roundabouts.
With various tools – raised or non-raised lane dividers, simple lane markings, – a turbo-roundabout is channeling vehicle movements in a narrower area than a regular multi-lane roundabout. In other words, vehicles' driving speed on the circulatory lane is lowered to guarantee maximum safety. Various research and experiments show that traffic accidents are reduced by 72% on turbo-roundabouts compared to multi-lane roundabouts, which makes turbo-roundabouts nearly as safe as single lane roundabouts.